- 首页 >> Research >> Research Progress
Research Progress
Progress in infrared photodetectors for multi-dimensional optical information acquisition in key laboratories of infrared science and technology
Recently, the associate researcher Xudong Wang's group from the State Key Laboratory of Infrared Physics have made a breakthrough in the field of multi-dimensional optical information acquisition. They proposed an innovative technology based on misaligned unipolar barrier photodetector (MUBP), providing new ideas for the development of infrared photodetectors. This achievement was published in the journal Nature Communications under the title “Multi-dimensional optical information acquisition based on a misaligned unipolar barrier photodetector”.
Infrared photodetectors play a crucial role in many fields such as night vision, astronomy, optical communications, health monitoring and remote sensing. At present, the development of infrared photodetectors focuses on integration and intelligence. The key to achieving this goal lies in using a single photodetector to obtain multi-dimensional optical information of the target, iincluding intensity, spectrum, polarization, etc. However, integrating spectral detection and polarization detection into traditional infrared photodetectors faces challenges in process and performance. The MUBP (non-aligned unipolar barrier photodetector) structure proposed by this research group uses a two-terminal barrier structure to achieve bias-switchable dual-spectrum detection through precise band engineering. Compared with three-terminal devices, two-terminal devices do not require additional common electrodes, have simple structures, simple manufacturing processes and high fill factors.
They used anisotropic semiconductors black phosphorus (bP) and black arsenic phosphorus (b-AsP) as the absorption layer, and molybdenum disulfide (MoS₂) as the barrier layer in the middle. The experimental results show that the photodetector can detect the polarization and spectrum of the target under forward bias and reverse bias respectively; using two absorption layers with different cutoff wavelengths, dual-spectrum detection is achieved; and blackbody response at room temperature is achieved at the same time. In addition, it shows higher accuracy and reliability in remote temperature measurement of dual-spectrum infrared photodetectors.
This research results were jointly completed by the Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study of the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences and Fudan University. Associate Researcher Xudong Wang from the State Key Laboratory of Infrared Physics, Young Associate Researcher Yan Chen and Professor Jianlu Wang from Fudan University are the corresponding authors of the paper. Postdoctoral fellow Shukui Zhang and Postdoctoral fellow Hanxue Jiao are the co-first authors of the paper. The research team said that they will continue to explore multi-dimensional optical information acquisition technology in depth and make greater contributions to promoting the development of photodetectors.
The research was supported by the Chinese Academy of Sciences B-type Pioneer Project, the National Natural Science Foundation, the Shanghai Science and Technology Commission, the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation and other projects.
Corresponding author: wxd0130@mail.sitp.ac.cn (Xudong Wang)
Paper link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-51378-7
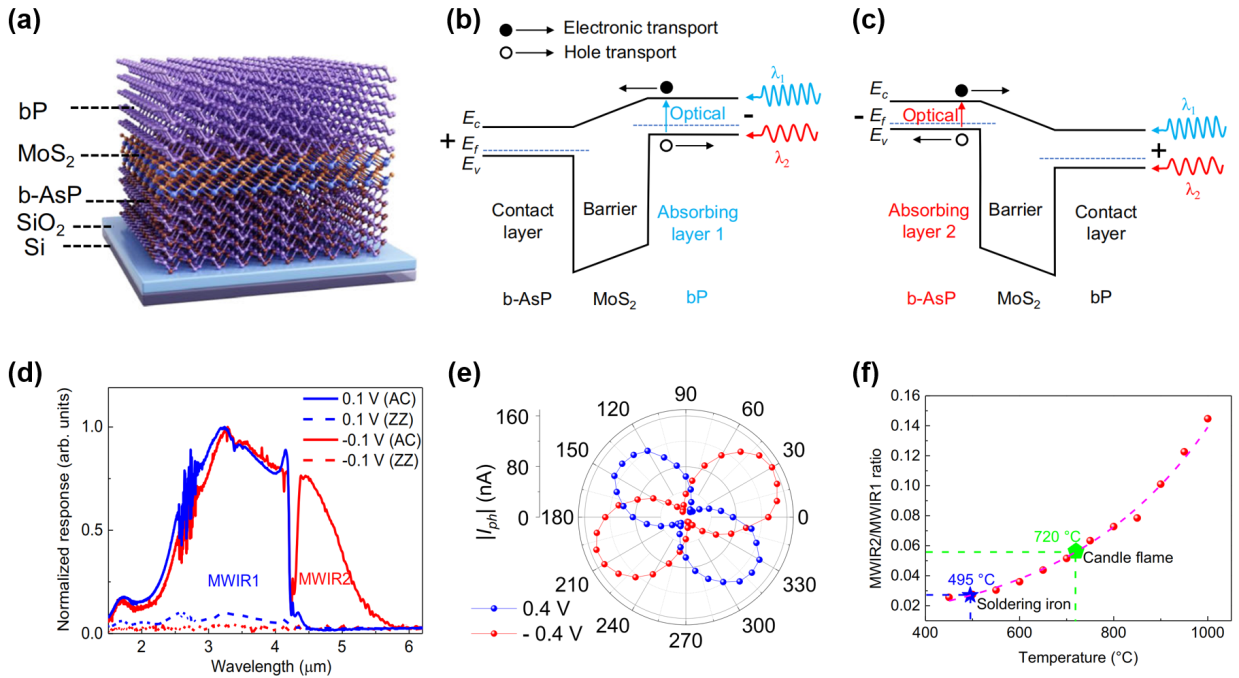
Figure 1. (a) Device structure of misaligned unipolar barrier photodetector (MUBP); (b-c) Schematic diagram of energy band structure of MUBP device under forward bias and reverse bias; (d) Dual-band spectral response of device MWIR1 and MWIR2 channels; (e) Polarization response characteristics of the device under forward bias and reverse bias; (f) Target temperature detection characteristics of the device.
